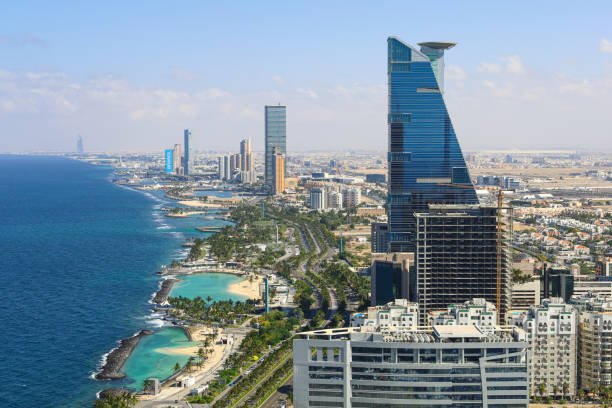

Jeddah to Tabuk Distance Guide
Jeddah and Tabuk are two fascinating places that attract tourists and people who are looking forward to the business opportunities in the Kingdom. Speaking of it, regardless of your commute, it would be more convenient


Luxury Hotelier | Travel Enthusiast
Few nations can claim to occupy 80% of an entire peninsula, yet Saudi Arabia stands as a testament to such geographical dominance. As Asia’s fifth-largest country, the Kingdom’s presence extends far beyond its physical boundaries, wielding influence across three continents through its unique position at the crossroads of ancient trade routes and modern commerce.
From the world’s largest contiguous sand desert to the sacred cities of Mecca and Medina, Saudi Arabia’s landscape tells a story of contrast and complexity. This fascinating nation has transformed from a collection of desert territories into a sophisticated state that shapes global energy markets, cultural exchange, and international diplomacy.
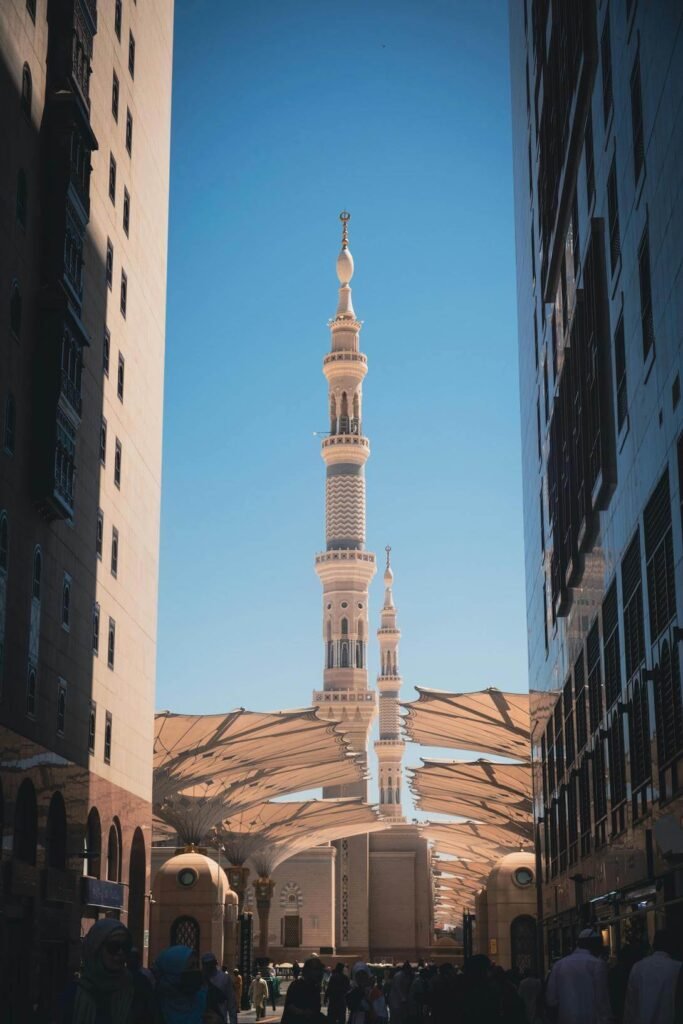

The foundations of contemporary Saudi Arabia were laid in 1727 through a transformative alliance between Muhammad ibn Saud and Muhammad ibn Abd-al-Wahhab. This partnership established the First Saudi State and introduced the Wahhabi movement, which would significantly shape the kingdom’s religious and cultural identity. The modern nation emerged through the remarkable unification campaign led by King Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman (Ibn Saud), culminating in the establishment of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia in 1932.
The kingdom’s continental significance is substantially amplified by its vast natural resources. As the world’s leading oil exporter, Saudi Arabia’s energy reserves have established it as an economic powerhouse across Asia and beyond. Beyond petroleum, the country’s wealth extends to diverse mineral deposits, including gold, phosphate, and uranium, strengthening its position as a resource-rich nation within the Asian continent.
Saudi Arabia’s rapid urbanisation has created powerful economic hubs that strengthen its continental ties. Major cities like Riyadh, Jeddah, and the holy cities of Mecca and Medina serve as crucial nodes in regional networks of commerce, culture, and spirituality. This urban development, coupled with modern infrastructure, has enhanced the kingdom’s ability to serve as a continental connector, facilitating movement of people, goods, and services across Asia.
The country’s membership in significant regional organisations, including the Gulf Cooperation Council, further cements its role as a key player in Asian affairs. Through Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia continues to leverage its geographic advantages and natural resources to strengthen its position as an integral driver of continental development and cooperation. This strategic vision focuses on transforming the kingdom’s unique position into tangible economic and diplomatic benefits, reinforcing its status as a pivotal Asian nation.
Saudi Arabia wields substantial influence in global markets, particularly through its dominant position in energy sectors. As the world’s leading oil exporter, the kingdom’s decisions significantly impact international energy prices and economic stability. Through strategic investments and economic diversification initiatives under Vision 2030, Saudi Arabia has expanded its influence beyond traditional oil markets into sectors like technology, entertainment, and sustainable development.
The kingdom’s role as custodian of Islam’s holiest sites makes it a pivotal destination for religious tourism, attracting millions of pilgrims annually for Hajj and Umrah. Beyond religious significance, Saudi Arabia has actively developed its cultural tourism sector through initiatives like the restoration of historical sites in Al-Ula and the ancient city of Diriyah. The establishment of the Ministry of Culture in 2018 has further enhanced the country’s appeal as a cultural destination, supporting various artistic and heritage projects.
Saudi Arabia’s global position is reinforced through strategic diplomatic relationships and international partnerships. The kingdom’s membership in key international organisations, including the G20, positions it as a crucial voice in global economic discussions. Its role in regional stability and security matters has made it an essential partner for nations worldwide, particularly in addressing Middle Eastern geopolitical challenges.
Through the General Authority for Entertainment and other cultural initiatives, Saudi Arabia has begun attracting international events, conferences, and performances, marking a significant shift in its global engagement strategy. These developments, combined with easier visa processes and enhanced tourism infrastructure, demonstrate the kingdom’s evolution into a more accessible and influential global player while maintaining its distinctive cultural identity.
Saudi Arabia offers visitors an array of unique cultural experiences, from exploring UNESCO World Heritage sites to participating in vibrant festivals. The restoration of historical landmarks like the al-Turaif district in Diriyah and the development of cultural hubs in cities like Al Ula provide authentic insights into the kingdom’s rich heritage. Tourists can now access previously restricted areas through an efficient e-visa system, making cultural exploration more accessible than ever.
Visitors must navigate distinct social customs and regulations while experiencing Saudi Arabia. Expatriates often reside in dedicated compounds offering modern amenities and a degree of cultural familiarity. Women visitors should note the requirement to wear appropriate attire in public spaces, though recent reforms have relaxed some traditional restrictions. Understanding and respecting local customs remains essential for a positive experience.
The kingdom’s rapid development has resulted in world-class infrastructure and facilities. Major projects like NEOM and Qiddiya Entertainment City showcase Saudi Arabia’s commitment to modern living standards. Transportation is well-developed, with excellent road networks, though public transport remains limited in some areas. International hotel chains provide high-quality accommodation, while entertainment options have expanded significantly with the lifting of the cinema ban and establishment of the Media City in Riyadh.
These developments reflect Saudi Arabia’s vision of becoming a major global tourism destination while maintaining its continental identity. The blend of traditional Arabian hospitality with modern amenities creates a unique experience for visitors, whether they come for business, leisure, or cultural exploration. The ongoing transformation under Vision 2030 continues to enhance the tourist and expatriate experience, making the kingdom increasingly attractive to international visitors while preserving its distinct cultural heritage.
As Saudi Arabia continues its ambitious journey under Vision 2030, its position as a continental powerhouse grows increasingly significant. The kingdom’s transformation from a traditional oil-dependent economy to a diverse, modern nation demonstrates its adaptability while maintaining its cultural heritage and religious significance.
The future holds promising developments as Saudi Arabia leverages its strategic location, natural resources, and cultural capital to strengthen its position in Asia and beyond. Through careful balance of tradition and innovation, the kingdom is poised to remain a crucial player in shaping the continent’s economic, cultural, and political landscape.

Jeddah and Tabuk are two fascinating places that attract tourists and people who are looking forward to the business opportunities in the Kingdom. Speaking of it, regardless of your commute, it would be more convenient

While most travellers dream of exploring well-trodden paths in Europe or Asia, Saudi Arabia emerges as the Middle East’s best-kept secret, welcoming an astounding 100 million visitors in 2023 alone. That’s why this guide covers
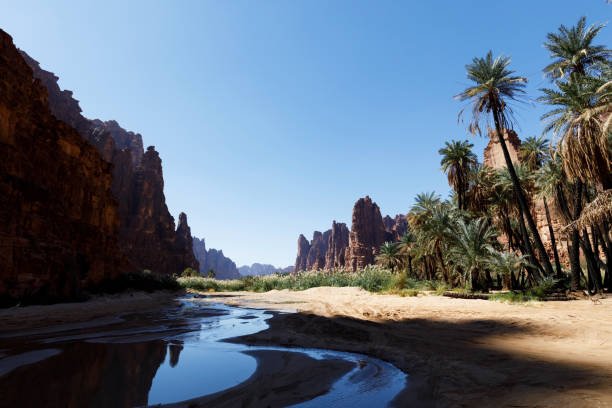

Tabuk City, nestled in the far northwestern corner of Saudi Arabia, is one of the Kingdom’s hidden gems. As Saudi Arabia continues its Vision 2030 transformation, Tabuk is stepping into the spotlight as a region
Source: USD/SAR @ Tue, 1 Jul.
© 2025 Sauditravelandleisure